title: generic win-form and web-form components (basolution)
author: babak ansari jaberi
email: babakansari@yahoo.com
member id: 36
language: c# 2.0
platform: windows, .net 2.0 etc
technology: asp.net, win froms/components, web forms/components
level: intermediate, advanced
description: a sample framework to create and use win-form and web-from generic components with the same controller to manipulate components behaviour on screen
license: <a href="%22%22%22%22../../info/licenses.aspx%22%22%22%22">cpol</a>
objective
the
objective of this solution is to introduce a framework to create
applications having both windows and web user interfaces with almost
the same look and feels.
introduction
all the
companies in the world (including software companies) looking for the
shortest possible path to produce more quality products (software) in
less time with the least possible resources (usually human experts).
code reuse has always been a challenge in software industry and one of
the key factors to get to the desire quality software with less time
and minimum resources. if a company can produce a windows-base and
web-base application in one product stream-line then there would be a
considerable return of benefits to the company. because producing these
two types of applications usually require two or three development
methods and each one have their own risks and considerations.
the
majority of software programs need to have user interface for human
interactions. there are various kinds of user interfaces for various
purposes. such as: windows-forms for quick and flexible access,
web-forms for internet access and so on. this article introduces a
software architect that can be used as a pfw (persistent framework) to
develop windows and web-base applications using the same business layer
and uip (user interface process) controller.
the goal in basolution
is to have ui components that are common to various kinds of user
interfaces so that developers can create and use those components,
without being worry about their behavior in different user interface
kinds. that means; having generic ui components. the generic components
are being access by the developers through a single interface. for
example: a generic textbox has a common text property in itextbox
interface that is common to both web and windows generic components.
obviously, there are some limitations to this approach, but depending
on application business needs, those limitations can also be mitigated.
even if you are using xaml, the components in xaml are having some
properties and events that are common in their meaning to the various
kinds of user interfaces.
analysis
what does basolution do?
in this framework; application developers do not need to be worry about
the kind of user interface they are developing application for, whether
it is windows form or web form. only component developers and
architects (core developers) need to know about the details of generic
components and they might need to make changes if they want to add more
functionality or adjust the ui behaviors according to business
developers need. so the product stream can be divided into two separate
lines:
- framework component (framework.development)
develop generic components and their behaviors
- business application (app.development)
use the generic framework components to create the user interface in depended from technologies (windows or web).
design
how does basolution work?
basolution is a framework in which all the user interface
functionalities are identified using interfaces. developing
applications in basolution requires .net development and interface
programming skills although conceptually it isn’t limited to any
technology.developing application is separated into two solutions:
- app.development to develop interfaces base on business needs.
identified as yellow color in following figure
- framework.development to develop components for both ui kinds.
identified as white color in following figure
|
windows form ui
(app.winform)
|
web form ui
(app.webform)
|
unit tests
(app.test)
|
data transfer object
(app.datasets)
|
framework common
(framework.lib)
(framework.bainterfaces)
(framework.ui.bacontroller)
(framework.ui.baresources)
|
|
(framework.ui.bawincontrols)
|
(framework.ui.bawebcontrols)
|
(framework.ui.bawincontrols)
|
|
ui controller
(app.controller)
|
|
business
(app.businesscontroller)
|
|
data access layer (dal)
(framework.dal)
| | |
(figure 3.2.1)
refer to the sample code: we have a form (geoform that implements
igeoform interface as in the example) with a bunch of components in it
(geotblgrid implements igrid, geotbltreeview implements itreeview and
entitycombo implements icombobox all inside igeoform). each form has a
controller object that implements an interface (igeoform) to hold and
use generic components that are being used in both windows and web. in
the controller; application developers implement ui behaviors and use
business logic layer and other services from the framework common to
all user interfaces. the layering architect is as follow:
- presentation
layer: a form/page that implements iform interface holding a reference
to a controller object that the form is being passed to it.
- controller
layer: each form/page has a controller object that works with generic
components provided from the form interface to the controller.
from the example: geoctrl controller object has a reference to the form
that implements igeoform interface to work with its generic components.
develop
as stated in the analysis, there can be two groups of developers
(application developers & core developers). like all other
technologies, application development is build on top of basolution
core and obviously the core is on top of .net framework and so on. each
developer group can have a proper framework solution set up to use
(refer to the sample program provided):
-
core developers:
develop and maintain generic components
1.1.
executable projects (win-form, web-form and unit test):
these projects can be executed independent from each other and can use
services provided from underneath layers and common components. all the
bacomponents are using binding mechanism to get and set data in the
component using binding relation, two groups of bonded components can
set up a master detail or parent child relations.
1.1.1.
windows form (winform) brings up the windows form that can access underneath common controller layer.
1.1.2.
web-form (webform) brings up the web form that can access to underneath common controller layer.
1.1.3.
unit test (test) brings up windows form access and execute its functionalities in various scenarios using common controllers.
1.2.
public library (lib) is basically a vertical layer that provides services to all other layers.
1.2.1.
framework.lib: functionalities common to all layers
1.2.2.
framework.bainterfaces: interfaces common to all layers
1.2.3.
framework.ui.bacontroller: common controllers
1.2.4.
framework.ui.baresources: resources used in all layers
1.3.
common horizontal layers
the layers below controller that is common to all kinds of user
interfaces. business layer uses data access layer (dal) to work with
underlying physical data access.
-
application (business) developers:
use generic components to develop
business related applications.
1.1.
develop applications to provide various user interface access to the application.
1.2.
use generic forms and components provided in ui layer
1.3.
implement business functionalities being used in each controller
how to use the basolution framework?
in
both windows and web solutions; we create a user interface folder (ui
folder) such as geofrm form in basefrm folder and in the both we should
identify the bacomponents we want to include in these pages using an
interface called igeoform. both ui holders should implement following
interface that has a bunch of bacomponent interfaces.
public interface igeoform
{
string caption{ get; set; }
itextbox geotblname{ get; }
igrid geotblgrid{ get; }
igrid entitytablegrid{ get; }
icombobox geotblkind{ get; }
iaddeditdelete addeditdel{ get; }
ibindingmanager bindingmanager{ get; }
ibindingmanager detailbindingmanager{ get; }
ibindingrelation bindingrelation{ get; }
itreeview geotbltreeview{ get; }
icombobox entitycombo{ get; }
itextbox entitytextbox{ get; }
iaddeditdelete addeditdeldetail{ get; }
}
for windows forms we have:
public partial class lookupform : form, igeoform
{
…
public lookupform()
{
geoctrl ctrl = new geoctrl(this, relationkind.lookup);
}
…
}
and for web-forms we have:
public partial class lookupform : webpagebase, igeoform
{
…
protected void page_load(object sender, system.eventargs e)
{
geoctrl ctrl = new geoctrl(this, relationkind.lookup);
}
…
}
for both of them we create an instance
of a controller implementing igeoform as stated in the above code (new geoctrl(this, relationkind.lookup)). the controller is responsible for
using the interfaces provided by generic components.
public class geoctrl
{
…
public igeoform theform;
public geoctrl(igeoform theform, relationkind kind)
{
this.theform = theform;
…
}
…
}

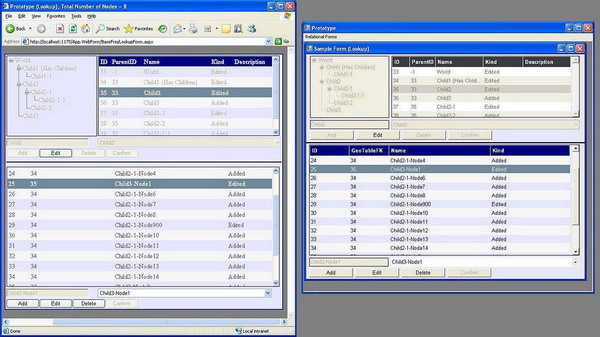
the figure shows all the generic components used in the provided
example. as stated in the diagram, all the visual components are bounded to one
non-visual binding manager component and binding managers are bounded to one
binding relation component to control their states (add, edit, delete or read-only).
summary
in order to create applications using basolution to have
both windows and web user interfaces, we should provide interfaces for each user
interaction component such as web/win components (igrid, itextbox, itextbox,…)
and forms/pages (igeoform). the user interface components can contain other generic
components (igeoform contains igrid, itextbox, itextbox,…).
a controller object can work with interfaces provided by each ui to implement business
functionalities. using generic components that are providing their method/property
and events using an interface has its own limitations that can be mitigated base
on business needs.
