This is the second part of the series where we learn how setup an Angular 2 with .NET Core
Introduction
This is the second part of this series. If you haven’t read the previous article, you can read it here.
In the first part of the series, we covered the following topics:
- Setup development environment for Angular 2
- Understand the structure of application
- Add Entity Framework in Project
- Create new pages to see the Employee List
- Perform Angular 2 routing
- Add Service
In this second and final part of series, we will cover the following topics:
- Add functionality to add a new employee
- Show the details of existing employee
- Edit details of existing employee
- Delete existing employee
- Add searching functionality to employee listing page
Let’s cover all the above points one by one.
Add New Employee
Home page of our application contains New Employee option in side menu. On click of this menu item, a new screen will open where we can add a new employee entry. We will create the following screen to add the details of a new employee.
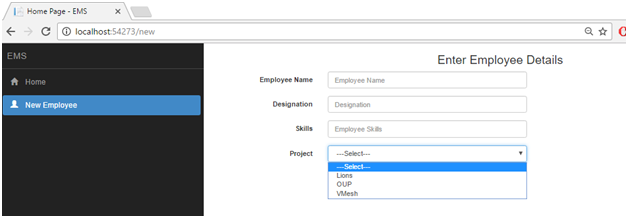
You can see that in add employee page, we have a dropdown for the projects list, so first of all, we need to create any API using which we can get the list of projects. For this, right click on Controller folder and a new API controller and named this controller as ProjectsController and paste the following code in this controller.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using EMS.Model;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EMS.Controllers
{
[Produces("application/json")]
[Route("api/Projects")]
public class ProjectsController : Controller
{
private readonly EmployeeContext _context;
public ProjectsController(EmployeeContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
[HttpGet]
public async Task<IActionResult> Get()
{
List<Project> project_ = new List<Project>();
var Project = await (from data in _context.Project
select new
{
ProjectId = data.ProjectId,
ProjectName = data.ProjectName
}).ToListAsync();
Project.ForEach(x =>
{
Project pro = new Project();
pro.ProjectId = x.ProjectId;
pro.ProjectName = x.ProjectName;
project_.Add(pro);
});
return Json(project_);
}
}
}
In the above code, we create an asynchronous method Get of "GET" type, and in this method, we are getting the list of all projects and return this list in JSON format.
Now open your services.ts file and paste the following code into this file:
getProjectList() {
return this.http.get('http://localhost:54273/api/projects');
}
In the above code, we create getProjectList method and in this method, we execute the get method of http class to get the project list.
Now open newEmployee.component.ts file and paste the following code into this file:
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { EmployeeServcies } from '../../Services/services';
import { Response } from '@angular/http';
import { FormGroup, FormControl, Validators } from '@angular/forms';
@Component({
selector: 'new-employee',
templateUrl: './newEmployee.component.html',
})
export class newEmployeeComponent {
public ProjectList = [];
public formData: FormGroup;
public constructor(private empService: EmployeeServcies) {
this.empService.getProjectList()
.subscribe(
(data: Response) => (this.ProjectList = data.json())
);
this.formData = new FormGroup({
'EmployeeName': new FormControl('', [Validators.required]),
'Designation': new FormControl('',Validators.required),
'Skills': new FormControl('', Validators.required),
'Project': new FormControl(0, [Validators.required, this.customValidator])
});
}
customValidator(control: FormControl): { [s: string]: boolean } {
if (control.value == "0") {
return { data: true };
}
else {
return null;
}
}
submitData() {
if (this.formData.valid) {
var Obj = {
Designation: this.formData.value.Designation,
EmployeeName: this.formData.value.EmployeeName,
ProjectId: this.formData.value.Project,
Skills: this.formData.value.Skills,
};
this.empService.postData(Obj).subscribe();
alert("Employee Inserted Successfully");
}
}
}
In constructor function, we create an instance of the EmployeeServcies class and call the getProjectList method to get the list of all projects and in response section, we insert the list of retrieved projects into ProjectList object of array type and later, we will bind this list to dropdown that shows the list of projects.
this.formData = new FormGroup({
'EmployeeName': new FormControl('', [Validators.required]),
'Designation': new FormControl('',Validators.required),
'Skills': new FormControl('', Validators.required),
'Project': new FormControl(0, [Validators.required, this.customValidator])
});
In the above line of code, we create a FormGroup and in this FormGroup, we create four form controls (EmployeeName, Designation, Skills and Project) and we will bind the formGroup to the form section that we will create in "html" section. The reason behind using the formGroup is that we want to use the data(model) driven approach instead of template driven to create the form section, because using the data(model) driven approach, we can create and apply custom validation easily. You can see that in "Project" FormControl, we implement two validations - the first one is required that is inbuilt validation and the second validation is customValidator - that is a custom validation. Below is the code of this validation:
customValidator(control: FormControl): { [s: string]: boolean } {
if (control.value == "0") {
return { data: true };
}
else {
return null;
}
}
In customValidator custom validator, we confirm that selected value of a control should now be 0. If value of value of control is 0, then we return the "true" as return value and this return value indicates the validation has been spoiled.
Now open your newEmployee.component.html file and paste the following code into this file:
<style>
.hidedata {
padding-top:50px;
}
</style>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<div class="col-md-8 col-lg-offset-4">
<h3>Enter Employee Details</h3>
</div>
<div class="row hidedata" id="hidDiv">
<div class="col-md-6 ">
<form class="form-horizontal" [formGroup]="formData"
(ngSubmit)="submitData()">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="EmployeeName" class="col-sm-4
control-label">Employee Name</label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input type="text" class="form-control"
name="EmployeeName" placeholder="Employee Name"
formControlName="EmployeeName" >
</div>
<div *ngIf="!formData.get('EmployeeName').valid &&
formData.get('EmployeeName').dirty"
class="col-sm-8 col-sm-offset-4"
style="color:red">
Add Employee Name
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="Designation" class="col-sm-4
control-label">Designation</label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input type="text" class="form-control"
name="Designation" placeholder="Designation"
formControlName="Designation">
</div>
<div *ngIf="!formData.get('Designation').valid &&
formData.get('Designation').dirty"
class="col-sm-8 col-sm-offset-4" style="color:red">
Add Employee Designation
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="Skills" class="col-sm-4 control-label">
Skills</label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input type="text" class="form-control"
name="Skills" placeholder="Employee Skills"
formControlName="Skills">
</div>
<div *ngIf="!formData.get('Skills').valid &&
formData.get('Skills').dirty"
class="col-sm-8 col-sm-offset-4"
style="color:red">
Add Skills of Employee
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="ProjectId" class="col-sm-4
control-label">Project</label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<select class="form-control" name="Project"
formControlName="Project" >
<option value="0">---Select---</option>
<option *ngFor="let data of ProjectList"
value={{data.projectId}}>
{{data.projectName}}
</option>
</select>
</div>
<div *ngIf="!formData.get('Project').valid &&
formData.get('Project').dirty"
class="col-sm-8 col-sm-offset-4"
style="color:red">
Select a Project for Employee
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-sm-offset-4 col-sm-8">
<button type="submit"
[disabled]="!formData.valid"
class="btn btn-info">Submit</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
In the above code, we create a form section and add total four controls (three textboxes and one dropdown) into this form section.
<form class="form-horizontal" [formGroup]="formData" (ngSubmit)="submitData()">
When you examine the above code, you will get [formGroup]="formData" line in form tag. The formGroup attribute is used to bind a form with formGroup object that we created into component section. Benefit of this approach is that when we submit this form, we get value of all the controls in a single formGroup object in key value pair.
<input type="text" class="form-control"
name="EmployeeName" placeholder="Employee Name"
formControlName="EmployeeName" >
The fromControlName directive syncs a "FormControl" in an existing "FormGroup" to a form control element by name. In other words, this directive ensures that any values written to the FormControl instance programmatically will be written to the DOM element (model -> view). Conversely, any values written to the DOM element through user input will be reflected in the FormControl instance (view -> model). In the above code, we syncs the EmployeeName form control to the EmployeeName element. In the same way, we wind all three existing the elements to "form control" of FormGroup.
<form class="form-horizontal" [formGroup]="formData" (ngSubmit)="submitData()">
In form tag, we implement the ngSubmit form event when form will be submit, it will call submitData method of component section. In submitData method, we implement the following code:
submitData() {
if (this.formData.valid) {
var Obj = {
Designation: this.formData.value.Designation,
EmployeeName: this.formData.value.EmployeeName,
ProjectId: this.formData.value.Project,
Skills: this.formData.value.Skills,
};
this.empService.postData(Obj).subscribe();
alert("Employee Inserted Successfully");
}
}
In the above code, first of all we check that form is in valid state or not, if form is in valid state, then we get the values from formData FormGroup and insert into JSON object and call the postData method of EmployeeService and pass the create object(Obj) as parameter.
Now open your Service.ts file and paste the following code into this file:
postData(empObj: any) {
let headers = new Headers({
'Content-Type':
'application/json; charset=utf-8'
});
let options = new RequestOptions({ headers: headers });
return this.http.post('http://localhost:54273/api/employee',
JSON.stringify(empObj), options);
}
In this code, we call the post method of http inbuilt service. We create a header and pass this header to post method of http service. We stringify the empObj and pass along with POST request. We are calling the POST method of Employee api controller. Now we need to add a POST method in our Employee API controller.
Add the following code into Employee controller:
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult AddEmployee([FromBody]Employee empObj)
{
_context.Employee.Add(empObj);
_context.SaveChanges();
return Json("OK");
}
In the above lines of code, we create an http post method and this method takes a parameter of employee type. We fetch out the parameter value from the FormBody of the request and add this employee object to the employee dbcontext and save the changes.
Now all setup is ready to add the new entry of employee, let’s try to add a new employee.

The above screen is showing the validation message, in case we break any validation conditions, then we get the corresponding error message.

If we don’t spoil any validation and press the Submit button, then we get the alert message of Employee Inserted Successfully. Now if you go to the home screen, you will find that entry of new employee into list.

Show Employee Details
In index view, we display the list of all employees and each employee entry also contains Detail button.

Using this button, we can get all information of an employee. Actually, this button is anchor tag in this anchor tag, we use the routerLink directive and passing details and employee id in URL. For example. if we click on Details button for Raj Kumar employee whose EmployeeID is 4, then "http://localhost:54273/details/4" URL will generate.
<a [routerLink]="['/details/',empData.employeeId]"
class="btn btn-primary">
Detail
</a>
We can retrieve the Employee details and on behalf of this Employee id. Now open details.component.ts file and add the following code into this file:
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { EmployeeServcies } from '../../Services/services';
import { Response } from '@angular/http';
import { Router, ActivatedRoute, Params } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'employee-detail',
templateUrl: './details.component.html'
})
export class DetailsComponent {
private EmpId: number;
public EmployeeDetails = {};
public constructor(private empService: EmployeeServcies,
private activatedRoute: ActivatedRoute) {
this.activatedRoute.params.subscribe((params: Params) => {
this.EmpId = params['id'];
});
this.empService.getEmployeeDetails(this.EmpId)
.subscribe((data: Response) =>
(this.EmployeeDetails["employeeName"] = data.json().employeeName,
this.EmployeeDetails["Designation"] = data.json().designation,
this.EmployeeDetails["ProjectName"] = data.json().projectName,
this.EmployeeDetails["Skills"] = data.json().skills,
this.EmployeeDetails["StartDate"] = data.json().startDate,
this.EmployeeDetails["EndDate"] = data.json().endDate
));
}
}
In the above code, we create an object of EmployeeServcies service in constructor function, we also create an instance of ActivatedRoute class, ActivateRoute is an observable of the URL segments matched by this route. Here, we subscribe this observable and get the value of id parameter that we defined during the routing.
In next line of code, we subscribe the getEmployeeDetails method of EmployeeService and pass the employee’s id as parameter whose details we want to get. Following is the code of getEmployeeDetails method and paste this code into your service.ts file.
getEmployeeDetails(empId: any) {
return this.http.get('http://localhost:54273/api/employee/' + empId);
}
In the above code, we call the get method of Employee API and pass the employee’s id parameter. In case of success, we fetched out the employee details from Response object and insert these details into EmployeeDetails object and bind this object to html template.
Now open details.component.html file and paste the following code into this file.
<h2>This is Detail Component</h2>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3"><b>Employee Name</b></div>
<div class="col-md-3">{{EmployeeDetails.employeeName}}</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3"><b>Designation</b></div>
<div class="col-md-3">{{EmployeeDetails.Designation}}</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3"><b>Skills</b></div><div class="col-md-3">
{{EmployeeDetails.Skills}}</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3"><b>ProjectName:</b></div><div class="col-md-3">
{{EmployeeDetails.ProjectName}}</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3"><b>Start Date</b></div><div class="col-md-3">
{{EmployeeDetails.StartDate|date: 'yMMMMd'}}</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3"><b>End Date</b></div><div class="col-md-3">
{{EmployeeDetails.EndDate|date: 'yMMMMd'}}</div>
</div>
Add following code into "EmployeeController.cs" file.
[HttpGet("{Empid}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> EmployeeDetails(int Empid)
{
var EmpDeatils = await(from emp in _context.Employee
join pro in _context.Project on
emp.ProjectId equals pro.ProjectId
where emp.EmployeeId==Empid
select new
{
emp.EmployeeId,
emp.EmployeeName,
emp.Designation,
pro.ProjectName,
emp.Skills,
pro.ProjectId,
pro.StartDate,
pro.EndDate
}
).FirstAsync();
return Json(EmpDeatils);
}
Here, we create a GET type method that takes one parameter of integer type. This parameter holds the id of employee and using this employee id, we get details of any employee and pass these details as JSON data. Following is the output of employee detail page.

Delete Employee Entry
In Employee listing page, we have an option with each employee entry to delete that employee entry. We add a click event listener on this anchor button and call the DeleteEmployee method on click event that take the employee’s Id as parameter.
<a
class="btn btn-danger" (click)="deleteEmployee
(empData.employeeId)">
Delete
</a>
Add the following lines of code in your home.components.ts file.
deleteEmployee(empId: number) {
var status = confirm("Are You want to delete this employee ?");
if (status == true) {
this.empService.removeEmployeeDetails(empId)
.subscribe((data: Response) =>
(alert("Employee Deleted Successfully")));
this.empService.getEmployeeList()
.subscribe(
(data: Response) => (this.EmployeeList = data.json())
);
}
}
When we click on Delete button, a confirmation box will be opened that confirms the deletion of the employee details and if status of confirmation box is true, then we call the removeEmployeeDetails method of EmployeeService class and pass the employeeId as parameter. Paste the following code into your service.ts file:
removeEmployeeDetails(empId: any) {
let headers = new Headers({
'Content-Type':
'application/json; charset=utf-8'
});
return this.http.delete('http://localhost:54273/api/employee',
new RequestOptions({
headers: headers,
body: empId
}));
}
In the above code, we call the delete method of employee api, so we needs to add a Delete method into our api that takes the employee’s id as parameter. Now open your EmployeeControler.cs file and paste the below lines of code:
[HttpDelete]
public IActionResult RemoveEmployeeDetails([FromBody]int empId)
{
Employee Emp;
Emp = _context.Employee.Where(x => x.EmployeeId == empId).First();
_context.Employee.Remove(Emp);
_context.SaveChanges();
return Json("OK");
}
In the above code, we create a method of http delete types that take an employee’s id as parameter that we are fetching from FormBody and using this employee id, we delete the record of that particular employee and send the OK as confirmation message.
Let’s try to record "Sandeep kumar Jangid" employee. When we click on Delete button, a confirmation box will open.

If you click on Ok button then, you will get Employee Deleted Successfully message.

After this confirmation message, you will find that employee list has been refreshed and deleted employee doesn’t exist in this list.

Update Employee Details
In employee listing page, we added an Edit button for each employee. When we click on this button, it will redirect to Edit Employee page and we are passing the EmployeeId as parameter.
<a [routerLink]="['/edit/',empData.employeeId]"
class="btn btn-success">
Edit
</a>
Now open editEmployee.component.ts file and paste the following code into this file:
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { EmployeeServcies } from '../../Services/services';
import { Response } from '@angular/http';
import { Router, ActivatedRoute, Params } from '@angular/router';
import { FormGroup, FormControl, Validators } from '@angular/forms';
@Component({
selector: 'edit-employee',
templateUrl: './editEmployee.component.html'
})
export class editEmployeeComponent {
private EmpId: number;
public EmployeeDetails = {};
public employeeName: string;
public ProjectList = [];
public formData: FormGroup;
public constructor(private empService: EmployeeServcies,
private activatedRoute: ActivatedRoute) {
this.activatedRoute.params.subscribe((params: Params) => {
this.EmpId = params['id'];
});
this.empService.getProjectList()
.subscribe(
(data: Response) => (this.ProjectList = data.json())
);
this.formData = new FormGroup({
'EmployeeId': new FormControl('', [Validators.required]),
'EmployeeName': new FormControl('', [Validators.required]),
'Designation': new FormControl('', Validators.required),
'Skills': new FormControl('', Validators.required),
'Project': new FormControl(0, [Validators.required, this.customValidator])
});
this.empService.getEmployeeDetails(this.EmpId)
.subscribe((data: Response) => (
this.formData.patchValue({ EmployeeId: data.json().employeeId }),
this.formData.patchValue({ EmployeeName: data.json().employeeName }),
this.formData.patchValue({ Designation: data.json().designation }),
this.formData.patchValue({ Skills: data.json().skills }),
this.formData.patchValue({ Project: data.json().projectId })
));
}
customValidator(control: FormControl): { [s: string]: boolean } {
if (control.value == "0") {
return { data: true };
}
else {
return null;
}
}
submitData() {
if (this.formData.valid) {
var Obj = {
EmployeeId: this.formData.value.EmployeeId,
Designation: this.formData.value.Designation,
EmployeeName: this.formData.value.EmployeeName,
ProjectId: this.formData.value.Project,
Skills: this.formData.value.Skills,
};
this.empService.editEmployeeData(Obj)
.subscribe((data: Response) =>
(alert("Employee Updated Successfully")));;
}
}
}
In constructor function, we create an instance of EmployeeServcies for accessing the HTTP method that we created. We also create an instance of ActivatedRoute to get the URL parameter values.
this.activatedRoute.params.subscribe((params: Params) => {
this.EmpId = params['id'];
});
In the above line of code, we fetched out the value of id parameter and save this value to EmpId variable.
this.empService.getProjectList()
.subscribe(
(data: Response) => (this.ProjectList = data.json())
);
We call the getProjectList method of EmployeeService class to get the project list and we use these values to bind the project dropdown list.
this.formData = new FormGroup({
'EmployeeId': new FormControl('', [Validators.required]),
'EmployeeName': new FormControl('', [Validators.required]),
'Designation': new FormControl('', Validators.required),
'Skills': new FormControl('', Validators.required),
'Project': new FormControl(0, [Validators.required, this.customValidator])
});
In the above code, we create an FormGroup and create total five FormControl into FormGroup. Here, we are going to perform the data(model) binding approach to bind a HTML form as similar as add new employee section.
this.empService.getEmployeeDetails(this.EmpId)
.subscribe((data: Response) => (
this.formData.patchValue({ EmployeeId: data.json().employeeId }),
this.formData.patchValue({ EmployeeName: data.json().employeeName }),
this.formData.patchValue({ Designation: data.json().designation }),
this.formData.patchValue({ Skills: data.json().skills }),
this.formData.patchValue({ Project: data.json().projectId })
));
In the above lines of code, we call the getEmployeeDetails method of EmployeeService class to get the inserted details of an employee and insert these details into formControl of formData. The patchValue method of formGroup is used to patch the value of FormControl of a formGroup in other words, patheValue method is used to match the value of FormControl. Here, we get the data from getEmployeeDetails method and insert this data into FormControl of the formGroup using patchValue method.
customValidator(control: FormControl): { [s: string]: boolean } {
if (control.value == "0") {
return { data: true };
}
else {
return null;
}
}
In the above line of code, we create an custom validator to validate the value of any control. It will set the invalid state of formGroup an formControl if the value of control is 0. Now open editEmployee.component.html file and paste the following code:
<style>
.hidedata {
padding-top: 50px;
}
</style>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<div class="col-md-8 col-lg-offset-4">
<h3>Edit Employee Details</h3>
</div>
<div class="row hidedata" id="hidDiv">
<div class="col-md-6 ">
<form class="form-horizontal" [formGroup]="formData"
(ngSubmit)="submitData()">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="EmployeeName"
class="col-sm-4 control-label">Employee Name</label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input type="text" class="form-control"
name="EmployeeName" placeholder="Employee Name"
formControlName="EmployeeName">
</div>
<div *ngIf="!formData.get('EmployeeName').valid &&
formData.get('EmployeeName').dirty"
class="col-sm-8 col-sm-offset-4" style="color:red">
Add Employee Name
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="Designation" class="col-sm-4 control-label">
Designation</label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input type="text" class="form-control"
name="Designation" placeholder="Designation"
formControlName="Designation">
</div>
<div *ngIf="!formData.get('Designation').valid &&
formData.get('Designation').dirty"
class="col-sm-8 col-sm-offset-4" style="color:red">
Add Employee Designation
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="Skills" class="col-sm-4 control-label">
Skills</label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input type="text" class="form-control"
name="Skills" placeholder="Employee Skills"
formControlName="Skills">
</div>
<div *ngIf="!formData.get('Skills').valid &&
formData.get('Skills').dirty"
class="col-sm-8 col-sm-offset-4" style="color:red">
Add Skills of Employee
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="ProjectId" class="col-sm-4 control-label">
Project</label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<select class="form-control" name="Project"
formControlName="Project">
<option value="0">---Select---</option>
<option *ngFor="let data of ProjectList"
value={{data.projectId}}>
{{data.projectName}}
</option>
</select>
</div>
<div *ngIf="!formData.get('Project').valid &&
formData.get('Project').dirty"
class="col-sm-8 col-sm-offset-4" style="color:red">
Select a Project for Employee
</div>
</div>
<div>
<input type="hidden" id="empId" name="empId"
formControlName="EmployeeId" />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-sm-offset-4 col-sm-8">
<button type="submit" [disabled]="!formData.valid"
class="btn btn-info">Submit</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
Here, we create an html form and bind this form to formGroup(formData) that we created in out component section. Functionality of this page is similar as the newEmployee.component.html page, so I think I don’t need to explain the code of this page. On submit action of the form, we call submitData method, below is the code of this method:
submitData() {
if (this.formData.valid) {
var Obj = {
EmployeeId: this.formData.value.EmployeeId,
Designation: this.formData.value.Designation,
EmployeeName: this.formData.value.EmployeeName,
ProjectId: this.formData.value.Project,
Skills: this.formData.value.Skills,
};
this.empService.editEmployeeData(Obj)
.subscribe((data: Response) =>
(alert("Employee Updated Successfully")));;
}
}
In the above lines of code, we get the value from formData that is FormGroup object and insert into new object(Obj). After that, we call the editEmployeeDatamethod of EmployeeService class and pass the previously created object as parameter.
Now open your service.ts file and paste the following code into this file:
editEmployeeData(empObj: any) {
let headers = new Headers({
'Content-Type':
'application/json; charset=utf-8'
});
let options = new RequestOptions({ headers: headers });
return this.http.put('http://localhost:54273/api/employee',
JSON.stringify(empObj), options);
}
In above method, we call the put method of Employee API to update the details of an employee and pass the update information of the employee. Now we need to create an method of PUT type in our API class that can get this update information and save these information into database, so open EmployeeController.cs file and paste the following code.
[HttpPut]
public IActionResult EditEmployee([FromBody]Employee empData)
{
_context.Entry(empData).State = EntityState.Modified;
_context.SaveChanges();
return Json("ok");
}
In the above code, we create a method of HTTP PUT type, in this method, we fetch out the data from the body of the request and save these changes to database for the permanent. Let’s try to edit the information of Dhramveer employee, when you click on edit button, the following screen will be open.

Now make some changes into existing information as follows:

When you click on Submit button, you will get an alert box of "Employee Updated Successfully" that means details of employee have been updated.

When you move to home page, you will find that details of employee have been updated.

Add Search Box
Now we add search functionality in our project, for this, we will add a textbox. Actually, we are going to add the filtering on Employee list. When we type any value in textbox, it will match that text to EmployeeName, Designation and Project field of an employee and return the employee details for whom entered text data matched at least on field of employee detail. In Angular 1.x, we have the filter for this type of the task but in Angular 2 and 4, we don’t have any such type of the filter. For this, Angular 2 comes with a new concept that is Pipe. Using the pipe, we can create our custom filter and implement wherever we want. Let’s create our custom filter using the Pipe.
For this go to App directory and create a new folder and name this folder as pipes. Now add a new typescript file in this folder and named this file as search.ts and paste the following code into this file.
import { Pipe,PipeTransform } from '@angular/core';
@Pipe({
name: 'searchFilter'
})
export class filterSearch implements PipeTransform {
transform(value: any, args: string): any {
if (args == null || args == undefined) {
return value;
}
else {
let filter = args.toLocaleLowerCase();
return filter ? value.filter(employee =>
(employee.employeeName.toLocaleLowerCase().indexOf(filter) != -1)
|| (employee.designation.toLocaleLowerCase().indexOf(filter) != -1)
|| (employee.project.toLocaleLowerCase().indexOf(filter) != -1)
) : value;
}
}
}
In the above lines of code, we define the @Pipe meta data that converts this class into a pipe object. The filterSearch class inherits the PipeTransform interface and we implement the transform method of interface into our filterSearch class. This method actually takes two parameters. First parameter contains the list data on which we will perform the filtering and second parameter contains the filter criteria. In the above code, we return the Employee details if any field(employeeName, designation and project) of employee contains the text of filter criteria.
After creating the Pipe, now we need to register this pipe in App.modules.ts file so register this pipe in app.modules.ts.

Now our pipe is ready and we have to register this pipe in app.modules.ts, last step is remaining to use this pipe in our code. Open your home.component.html file and replace the content of this page with the following content.
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h3>Employee List</h3>
<br />
</div>
<div class="col-md-12">
<div class="form-actions no-color">
<div>
<span style="font-weight:bold;font-size:20px">Search:</span>
<input type="text" name="searchdata" #search (keyup)="0"/>
</div>
</div>
<br />
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="table-responsive">
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>
S.No.
</th>
<th>
EmployeeName
</th>
<th>
Designation
</th>
<th>
Project
</th>
<th>
Action
</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr *ngFor="let empData of EmployeeList |
searchFilter:search.value ; let i = index; trackBy: employeeId">
<td>
{{i+1}}
</td>
<td>
{{empData.employeeName}}
</td>
<td>
{{empData.designation}}
</td>
<td>
{{empData.project}}
</td>
<td>
<a [routerLink]="['/details/',empData.employeeId]"
class="btn btn-primary">
Detail
</a>
<a [routerLink]="['/edit/',empData.employeeId]"
class="btn btn-success">
Edit
</a>
<a
class="btn btn-danger"
(click)="deleteEmployee(empData.employeeId)">
Delete
</a>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</div>
In the above code, I make only two changes, the first one is add a textbox and bind local template variable with this textbox (#search).
<div class="col-md-12">
<div class="form-actions no-color">
<div>
<span style="font-weight:bold;font-size:20px">Search:</span>
<input type="text" name="searchdata" #search (keyup)="0"/>
</div>
</div>
<br />
</div>
The second change is that we implement the pipe that we created on employee list and pass the value of local template variable (search) as filtering criteria.
<tr *ngFor="let empData of EmployeeList | searchFilter:search.value ;
let i = index; trackBy: employeeId">
After making all the changes, now our screen will look like below:

Now if we enter any text into textbox, it will filter the employee list and only show the employee details who match the filtering criteria.

Summary
This is the second and last part of this series. I hope you liked this series. During this series, we learn how to setup an Angular 2 with .NET Core. We implement the Code first approach of the Entity Framework and setup the database connection. We perform the CRUD operations that are the basic learning step of any technology. We learn how to create and implement the services in Angular2, we also learn about the Pipe and create our custom pipe to implement the filter functionality in our project. If you have any query regarding this series or Angular 2 and .NET Core, then write in the comment section. If you want to download this project, then you can go to this Github repository.
History
- 19th April, 2017: Initial version
